Cannabis and anxiety

Cannabis and anxiety
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is the most common mental health disorder in our society. In 2017, and according to the WHO, about 264 million people around the world lived with anxiety disorders of different degrees.
Anxiety is characterized by an alteration of how we process emotions and behave. Those who suffer from anxiety live with excessive tension and worried thoughts and are unable to solve most issues, make choices or communicate, among other things, like most people do.
Anxiety comprises a variety of different disorders also with different degrees of intensity, ranging from social anxiety and panic disorders to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and agoraphobia.
What is the conventional treatment of anxiety?
There are currently three main strategies to treat anxiety.
1-Therapy: Psychoanalysis is used to better understand the root of the conflict.
2-Medication: Mainly anxiolytic drugs.
3-Meditation, yoga, mindfulness: It is mainly used to complement medication in order to reduce stress.
Nevertheless, the current treatment of anxiety causes many side effects, develops habituation and it is not recommended to treat children.
How anxiety works within our brain?
Inside our brain, anxiety is caused by an alteration of the communication pathways between neurons, in particular of those neurons involved in the management of emotions. The area of the brain that manages emotions, learning and memory is known as the Limbic system (Fig. 1), which comprises several structures such as the hippocampus and the amygdala, among others.
The amygdala is responsible for our sexual behavior, hormonal control, reaction to fear, aggressiveness, emotional learning, emotional memory, etc. The hippocampus is related to the management of emotions, long-term memory and learning.
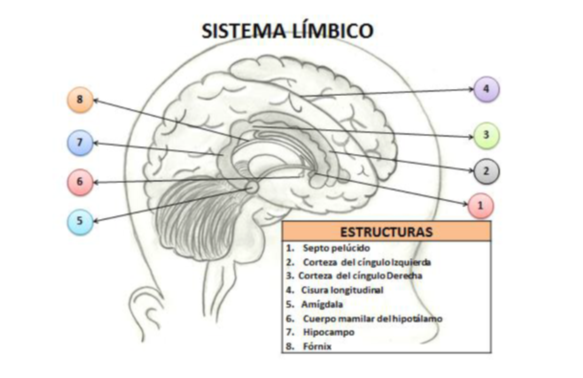
Figure 1: Components and structures of the limbic system. Adapted from Saavedra-Torres, Morfolia, 2015.
Traducció de la figura
Limbic System
- Septum pellucidum
- Left cingulate cortex
- Right cingulate cortex
- Longitudinal fissure
- Amygdala
- Mammillary bodies
- Hypocampus
- Fornix
How do we generate emotional memory?
The generation of memories and memory itself in our brain has been studied for years. It is known that memory consolidates in certain areas of the brain by means of chemical processes that involve the release and uptake of neurotransmitters.
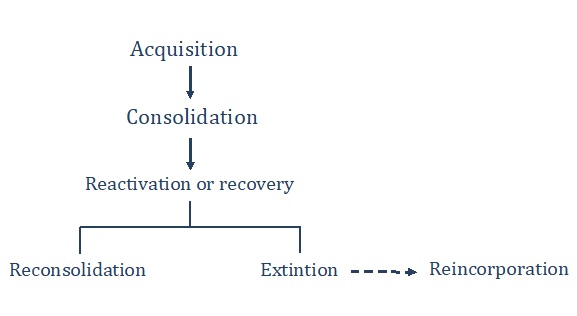
Figure 2: Stages of emotional memory. Adapted from Stern et al. 2018.
Cannabis and anxiety. How can medical Cannabis relieve anxiety?
It has been reported that trauma or stress alter our memory and generate divergent memories. In response to a negative event there is always an emotional exacerbation which usually has a neutral effect on healthy individuals but may generate stress, anxiety or fear in sick people.
These mechanisms are mediated by several neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, whose levels fluctuate in individuals suffering from depression (very low serotonin levels) or anxiety (low levels of serotonin).
We know now that Cannabis and anxiety have these links. Endocannabinoids are capable of activating the release and uptake of neurotransmitters in neurons. Furthermore, the presence of cannabinoid receptors within several areas of the limbic system, especially CB1 in the amygdala and the hippocampus, has been reported, suggesting that endocannabinoids might have a role in the development of memory and learning.
Several studies in both humans and animals have shown that compounds whose activity is mediated by CB1 receptors are capable of reducing negative memories by promoting their extinction and/or impairing their consolidation as negative emotional memories (Figure 3).
In this regard, the reconsolidation of memory rises as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of mental disorders associated with a poor adaptation of emotional memory.
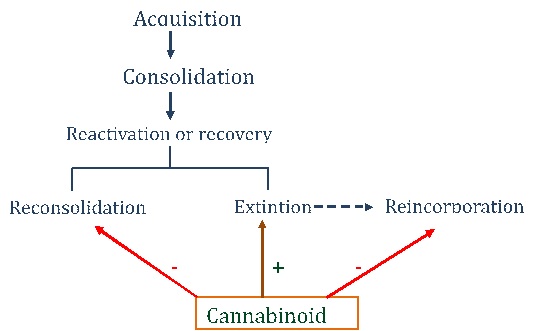
Figure 3: Stages of emotional memory: effect of cannabinoids. Adapted from Stern et al., Neuroscience, 2018.
Cannabidiol or CBD acts in the brain by interacting with the CB1 endocannabinoid receptors or by means of an indirect effect on additional neurotransmitter receptors, such as the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A, among others (see Biology of Cannabis, Degroot et al., 2018).
Since 1984 there are plenty of studies performed both in humans and animals that describe the anxiolytic effect of cannabinoids (reduce anxiety). Recent studies in patients with social anxiety disorder (SAD) have shown that the administration of a single CBD dose suffices to reduce anxiety, discomfort and cognitive impairment in these patients (Bergamaschi et al., 2011). There is also a report that described its use for the treatment of anxiety and insomnia resulting from post-traumatic stress in children, and the chronic administration of CBD oil produced a decline of the symptoms (Shannon et al., 2016).
Given all the scientific evidence that shows the active expression of the endocannabinoid system within the brain and, particularly, within areas related to memory and emotional control, the mechanisms of action of cannabinoids on anxiety and stress could be mediated by several chemical processes that also affect neurotransmitter receptors such as serotonin, glutamine or acetylcholine, or even directly on endocannabinoid receptors.
Both theories coexist but, in both cases, the final consequence is the modulation of anxiety and stress, relieving people suffering from these disorders and allowing them to carry on with a much more stable and pleasant life.
References Cannabis and anxiety
1-Shannon et al, 2016. Effectiveness of cannabidiol oil from pediatric anxiety and Insomnia: Case Report
2-Crippa et al, 2010. Neural basis of anxiolytic effects of cannabidiol (CBD) in generalized social anxiety disorder
3-Stern at al, 2018. Effects of cannabinoid drugs on aversive or rewarding drug-associated memory extinction and reconsolidation
4-Bergamaschi et al, 2011. Cannabidiol reduce the anxiety induced by simulated public speacking in treatment-naïve social phobia patients.
5-Deroot, 2018. Role of Cannabidiol receptor in anxiety disorders.
6- Saavedra-Torres JS, et al. 2015. Correlación funcional del sistema límbico con la emoción, el aprendizaje y la memoria
7-https://www.depressionalliance.org/

 PACK Sérum y Crema Facial con CBD
PACK Sérum y Crema Facial con CBD 




Responses